How Many Active Volcanoes Are In The US?
The United States is home to one of the most volcanically active landscapes on Earth, ranking third globally behind Indonesia and Japan. So, how many active volcanoes are in the US? The answer might surprise you.
As of 2025, the United States has 169 active volcanoes, according to the US Geological Survey (USGS). These volcanoes are primarily located in regions with significant tectonic activity, such as Alaska, Hawaii, and the Pacific Northwest. Many of these volcanoes have erupted in the recent past and will erupt again in the foreseeable future. As populations increase, areas near volcanoes are being developed, and aviation routes are increasing, putting more people and property at risk from volcanic activity.
These geological giants are more than just ticking time bombs; they’re fundamental forces that shape ecosystems, fuel scientific research, and even draw curious travelers.
Take a look at where these volcanoes are, what makes them active, and the specific peaks that continue to smolder, hiss, and remind us of the raw power beneath our feet.
What Is An Active Volcano?
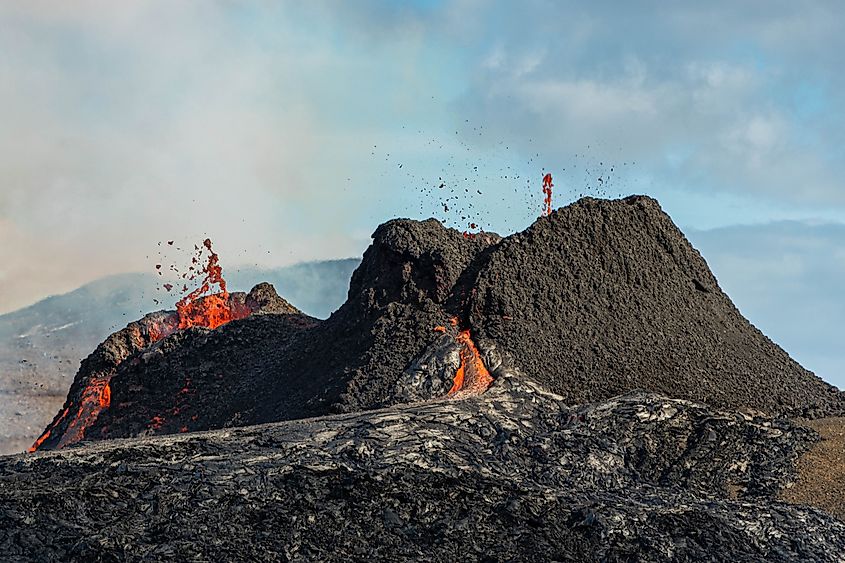

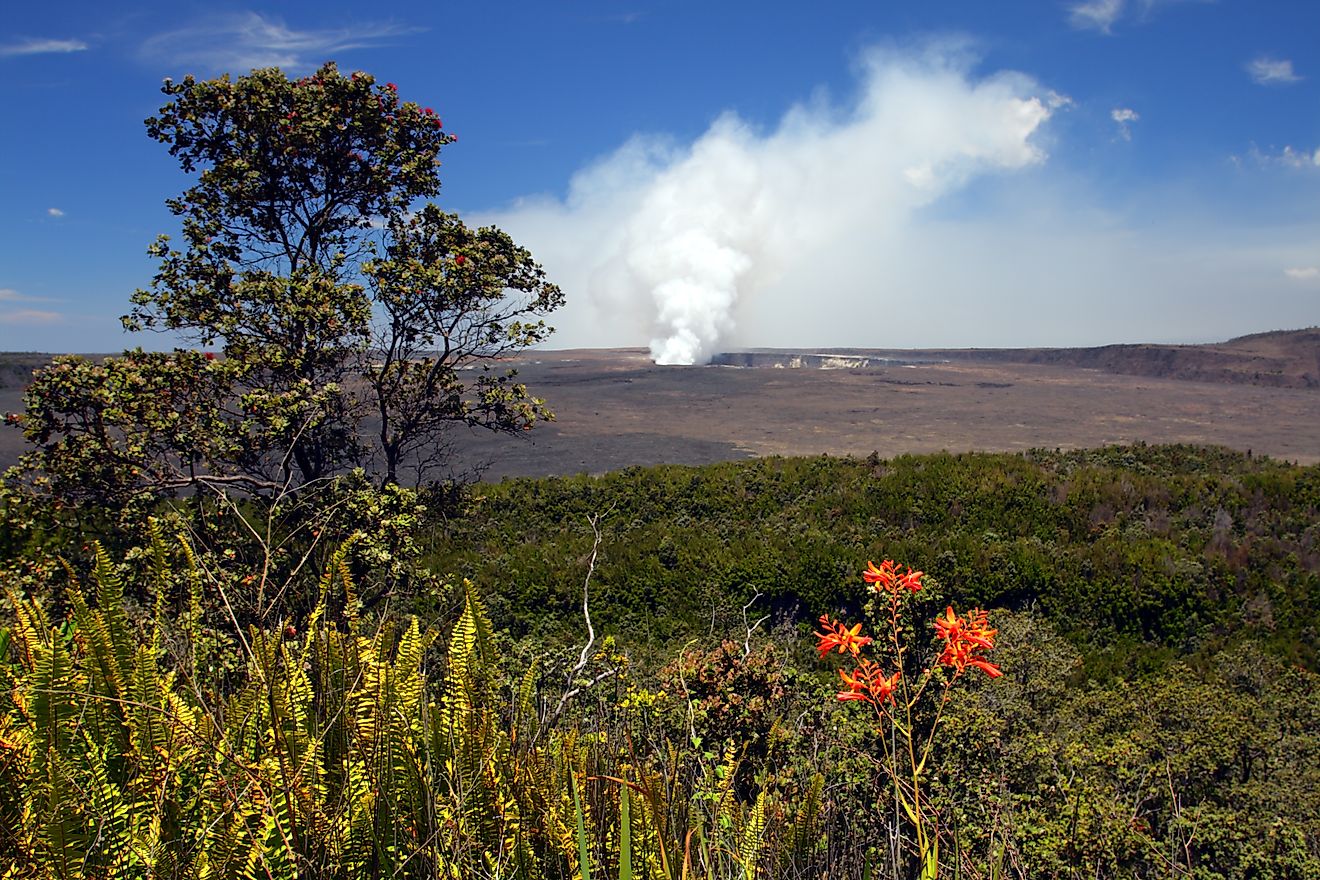
Kilauea volcano in Hawaii.
In volcanology, a volcano is considered "active" if it has erupted during the Holocene Epoch (the last 11,700 years) and shows signs of potential future eruptions. These signs can include seismic activity, gas emissions, ground deformation, or thermal anomalies. It's important to note that an active volcano doesn't necessarily mean it's erupting at this very moment; rather, it indicates that the volcano has the potential to erupt again.
Volcanoes that have not erupted for thousands of years but are not considered extinct are classified as dormant. Extinct volcanoes are those that geologists believe will never erupt again due to a lack of magma supply or tectonic activity.
Alaska
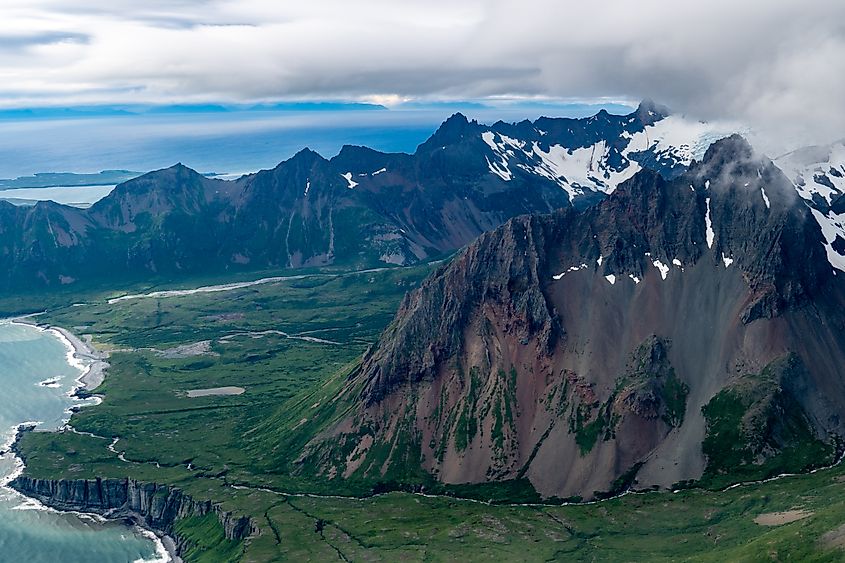

Aerial view of the volcanoes and Aleutian Range of mountains in Southwest Alaska.
Alaska boasts the highest concentration of active volcanoes in the United States, with more than 130 identified. The state sits along the Pacific Ring of Fire, where the Pacific Plate collides with the North American Plate, creating frequent volcanic activity. Many of Alaska’s volcanoes are remote, but their eruptions can impact air travel, local ecosystems, and global atmospheric conditions. Notable active volcanoes in Alaska include:
- Mount Redoubt: An active stratovolcano in the Aleutian Range, Mount Redoubt erupted in 2009, sending ash plumes thousands of feet into the sky. The eruption disrupted air traffic, contaminated rivers with volcanic debris, and underscored the hazards posed by Alaska’s remote but powerful volcanoes. Continuous monitoring tracks seismic activity, gas emissions, and ground deformation.
- Mount Spurr: Located near Anchorage, Mount Spurr has a history of explosive eruptions and has shown signs of increased activity in recent years. Its proximity to populated areas makes monitoring essential, and scientists use advanced technology to track potential hazards and ensure public safety.
- Great Sitkin Volcano: Situated on an uninhabited island in the Aleutian chain, Great Sitkin erupted in 2021, highlighting the ongoing dynamism of Alaska’s volcanic landscape. Remote though it may be, its eruptions serve as critical data points for understanding Aleutian volcanism and global volcanic activity.
- Other Notable Volcanoes: Alaska’s volcanic network includes Mount Iliamna, Mount Okmok, and Mount Pavlof, each with a history of eruptions that contribute to the state’s geologic diversity. These volcanoes create unique landscapes, including lava flows, calderas, and ash deposits, and they provide valuable insight into the Pacific Ring of Fire’s activity.
Hawaii
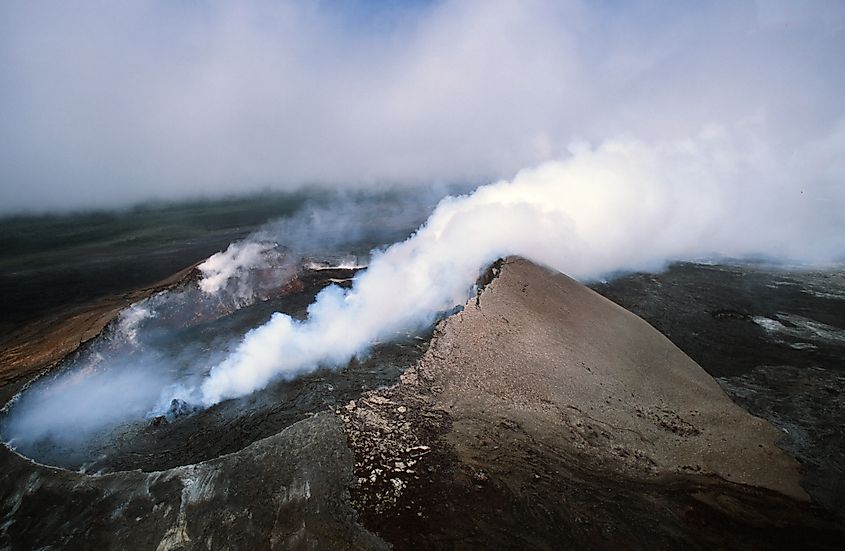

Hawaii is another hotspot for volcanic activity, primarily due to the Hawaiian hotspot, a stationary plume of hot material rising from deep within the Earth's mantle. This hotspot has created a chain of volcanic islands over millions of years, producing some of the most studied and closely monitored volcanoes on Earth. Active volcanoes in Hawaii include:
- Kīlauea: One of the world's most active volcanoes, Kīlauea has been erupting frequently for decades. Its continuous lava flows since 1983 have reshaped the Big Island's landscape, destroying property, creating new land, and offering scientists a rare opportunity to study active volcanic processes up close.
- Mauna Loa: The largest volcano on Earth by volume and area, Mauna Loa dominates the Big Island. Its most recent eruption occurred in 2022 after 38 years of dormancy. Mauna Loa's massive size means eruptions can impact large areas, with lava flows capable of reaching the ocean and influencing local ecosystems.
- Mauna Kea: Although considered dormant, Mauna Kea is the tallest mountain in the world from base to summit when measured from the ocean floor. Its summit is home to world-class astronomical observatories and provides unique insight into the long-term evolution of Hawaiian volcanoes.
Pacific Northwest
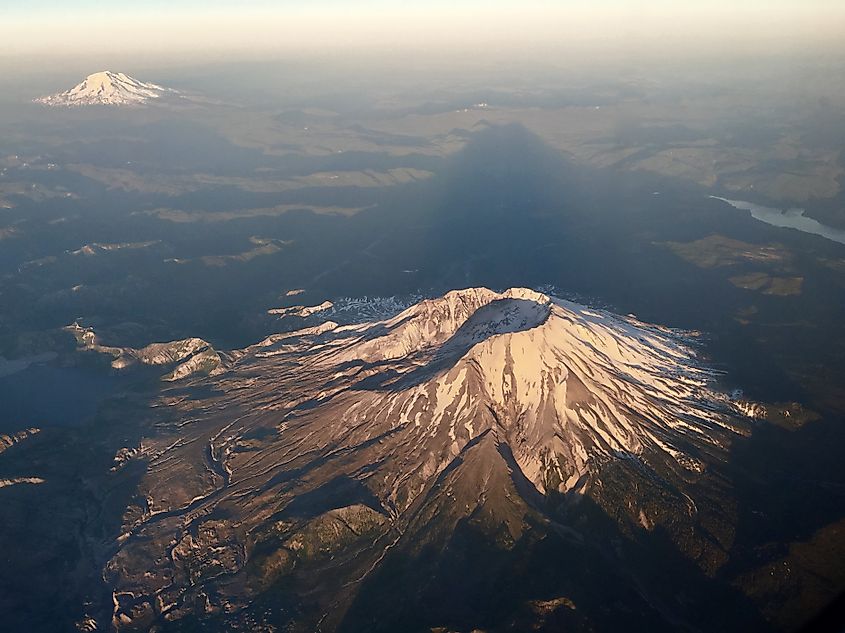

The Pacific Northwest, particularly the Cascade Range, is home to several active volcanoes. This region sits along the boundary where the Juan de Fuca tectonic plate is subducting beneath the North American Plate, creating ideal conditions for volcanic activity. Active and potentially active volcanoes in the Cascade Range include:
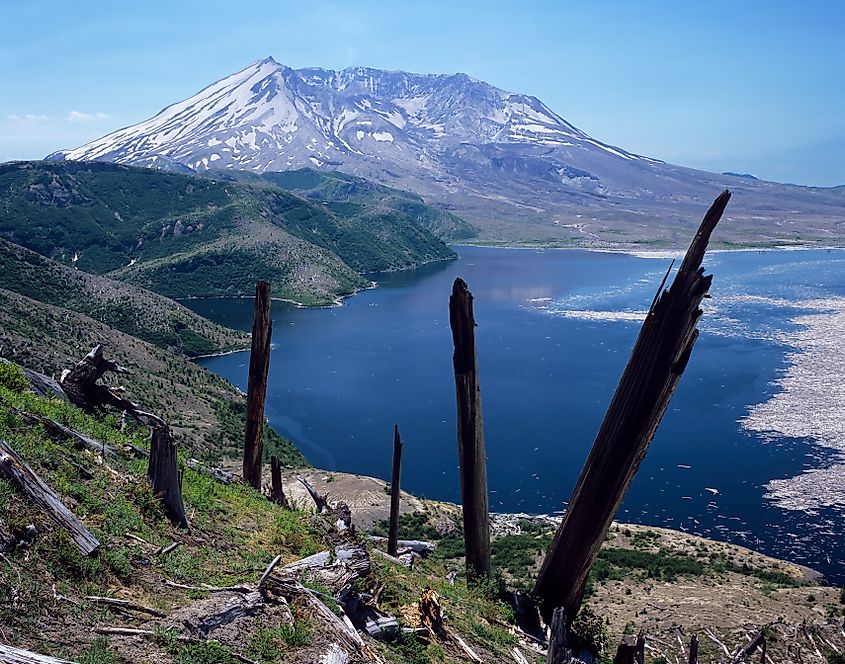
- Mount St. Helens: Famous for its catastrophic eruption in 1980, Mount St. Helens remains one of the most closely monitored volcanoes in the United States. Its eruption reshaped the surrounding landscape, creating a large crater and triggering lahars, landslides, and widespread ashfall. Seismic activity and gas emissions continue, making it a focal point for volcanic research and hazard preparedness.
- Mount Rainier: While currently dormant, Mount Rainier is considered active due to the potential for future eruptions. It is heavily glaciated, with over 25 major glaciers, which could transform an eruption into dangerous lahars that threaten nearby communities, including the Seattle metropolitan area. Rainier’s snow and ice contribute to its ongoing geological activity and make it a unique study site for volcanologists.
- Mount Hood: The highest peak in Oregon, Mount Hood has displayed fumarolic activity and minor seismic events, signaling the potential for future eruptions. Its stratovolcano structure dominates the landscape and has a history of explosive eruptions, lava flows, and lahars that continue to shape the surrounding valleys.
California
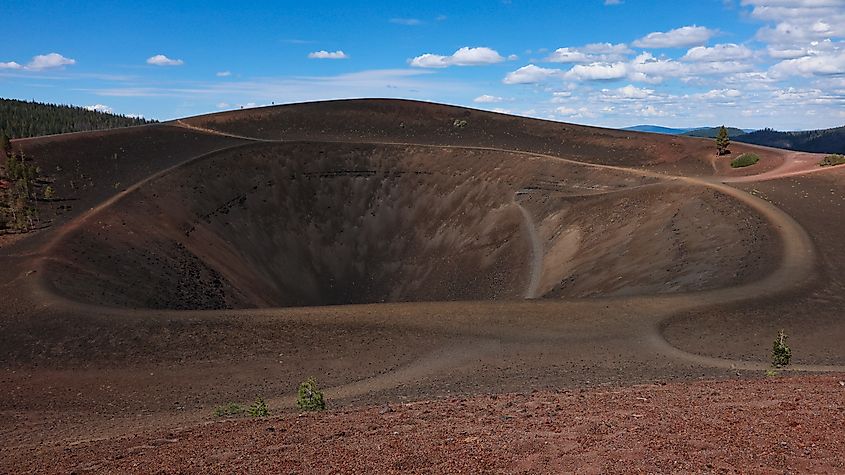

California is home to several notable volcanic sites. The Lassen Volcanic Center last erupted between 1914 and 1917, producing lava flows, ash clouds, and dramatic landscape changes that are still visible today. Lassen Peak itself rises prominently above the surrounding terrain, offering scientists a rare opportunity to study a volcano that erupted in the 20th century.
Another major feature is the Long Valley Caldera, a massive volcanic system in eastern California. While it has not erupted recently, the area exhibits ongoing geothermal activity, including hot springs and fumaroles, indicating that magma remains beneath the surface. Both sites are closely monitored for signs of future activity.
Oregon
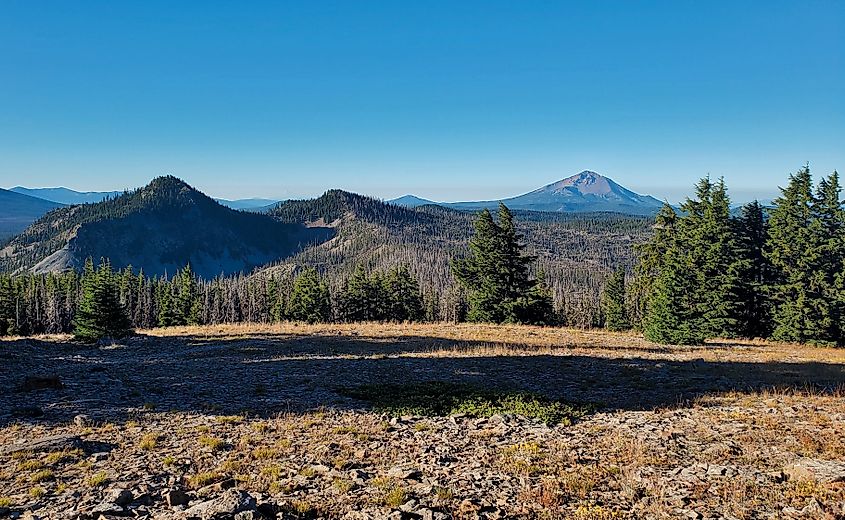

Oregon hosts multiple active volcanoes, primarily within the Cascade Range. Mount Hood, the state’s tallest peak, shows fumarolic activity and minor seismic events, signaling its potential for future eruptions. The Three Sisters, a cluster of volcanic peaks in central Oregon, are also under constant observation. These volcanoes have shaped Oregon’s landscape over hundreds of thousands of years, creating lava flows, valleys, and fertile soils. Due to their proximity to populated areas and critical infrastructure, scientific monitoring is essential to detect early warning signs of volcanic unrest.
American Samoa
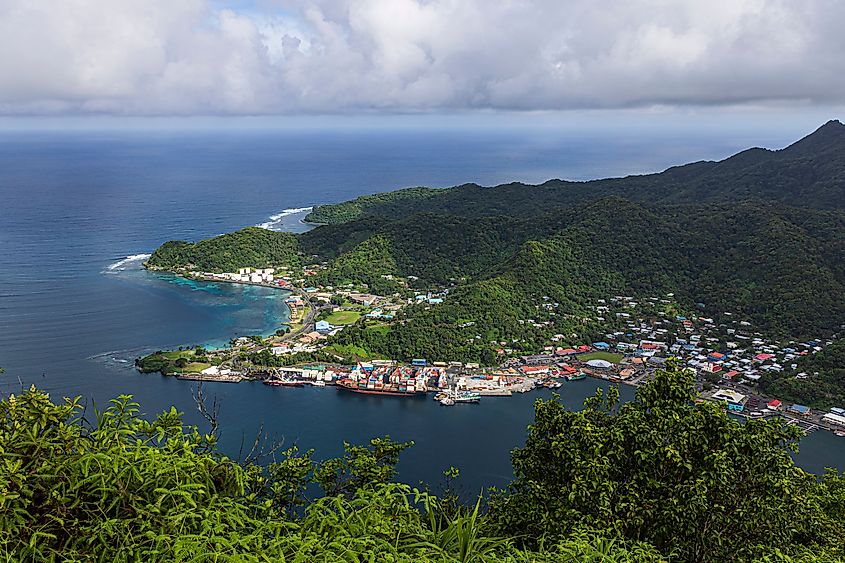

The US territory of American Samoa in the South Pacific is part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, making it volcanically active. The island of Ta‘ū is a prominent example, featuring volcanic formations and recent lava flows that illustrate the ongoing geological activity in the region. Though remote, these volcanoes impact local communities and ecosystems and provide valuable insight into hotspot volcanism in the oceanic Pacific. American Samoa’s volcanic activity is also an important natural laboratory for studying island formation and volcanic hazards in tropical environments.
The Most Dangerous Volcanoes in the US

Some US volcanoes pose greater risks due to their eruption history, size, or proximity to people.
- Mount Rainier, Washington: Glacial coverage makes lahars a major threat to communities downstream.
- Yellowstone Caldera, Wyoming: A supervolcano capable of massive eruptions, closely monitored for ground swelling and seismic activity.
- Mount St. Helens, Washington: Known for its 1980 eruption, it remains active with ongoing seismic activity and dome growth.
- Mauna Loa, Hawaii: The largest volcano on Earth, capable of destructive lava flows, as seen in its 2022 eruption.
- Long Valley Caldera, California: Still active with geothermal activity, scientists watch for earthquakes and ground deformation.
These volcanoes show the variety of hazards in the US, from lava and mudflows to ash clouds, making monitoring essential for safety.
Living with Fire: Understanding America’s Volcanoes
Volcanoes in the United States are more than geological features; they are dynamic forces shaping landscapes, ecosystems, and communities. From the towering peaks of the Pacific Northwest to the fiery islands of Hawaii and the supervolcano beneath Yellowstone, each eruption tells a story of power, adaptation, and change. Active monitoring, scientific research, and preparedness help communities coexist with these natural giants, turning potential hazards into opportunities for learning and understanding.
Studying US volcanoes offers insight into Earth’s inner workings, informs disaster planning, and highlights the resilience of humans and nature alike. While eruptions can be destructive, they are also a reminder of the planet’s energy, creativity, and ongoing evolution. America’s volcanoes continue to fascinate, challenge, and inspire, showing that the land beneath our feet is never as still as it seems.
Quick Facts About Volcanoes in the US
-
The United States has 169 active volcanoes as of 2025, according to the USGS.
-
Alaska contains more than 130 of them, the highest concentration in the country.
-
Hawaii’s Kīlauea is one of the most active volcanoes in the world, reshaping the Big Island with frequent eruptions.
-
The Cascade Range in the Pacific Northwest includes Mount St. Helens, Mount Rainier, and Mount Hood, all closely monitored for activity.
-
California’s Lassen Peak last erupted between 1914 and 1917, while the Long Valley Caldera shows ongoing geothermal unrest.
-
American Samoa’s volcanic activity, including on the island of Ta‘ū, connects it to the Pacific Ring of Fire.
-
The most dangerous US volcanoes include Mount Rainier, Mount St. Helens, Mauna Loa, Yellowstone Caldera, and Long Valley Caldera.
-
Volcanic eruptions can affect aviation, local communities, and even global climate through ash and gas emissions.