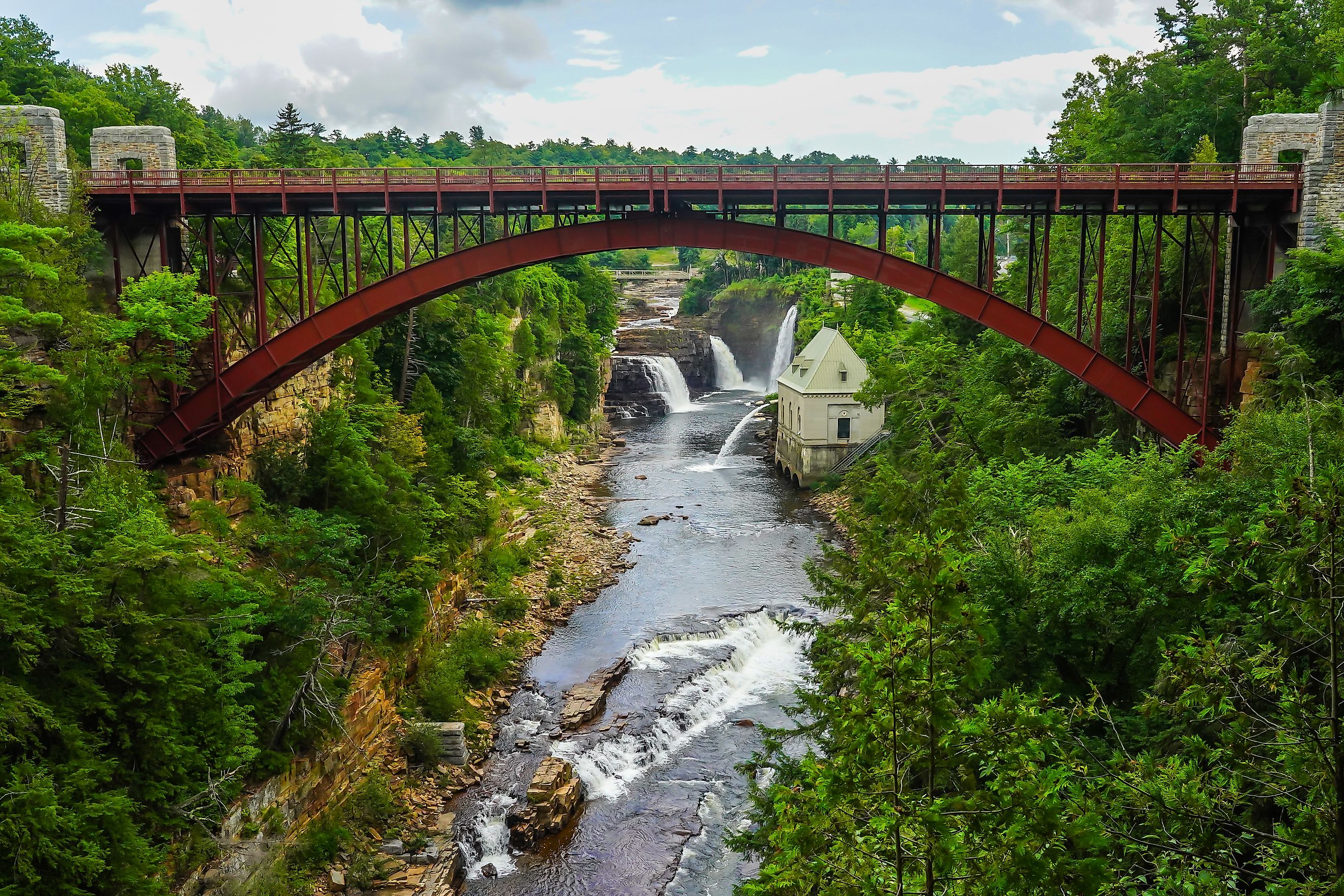
Upstate New York
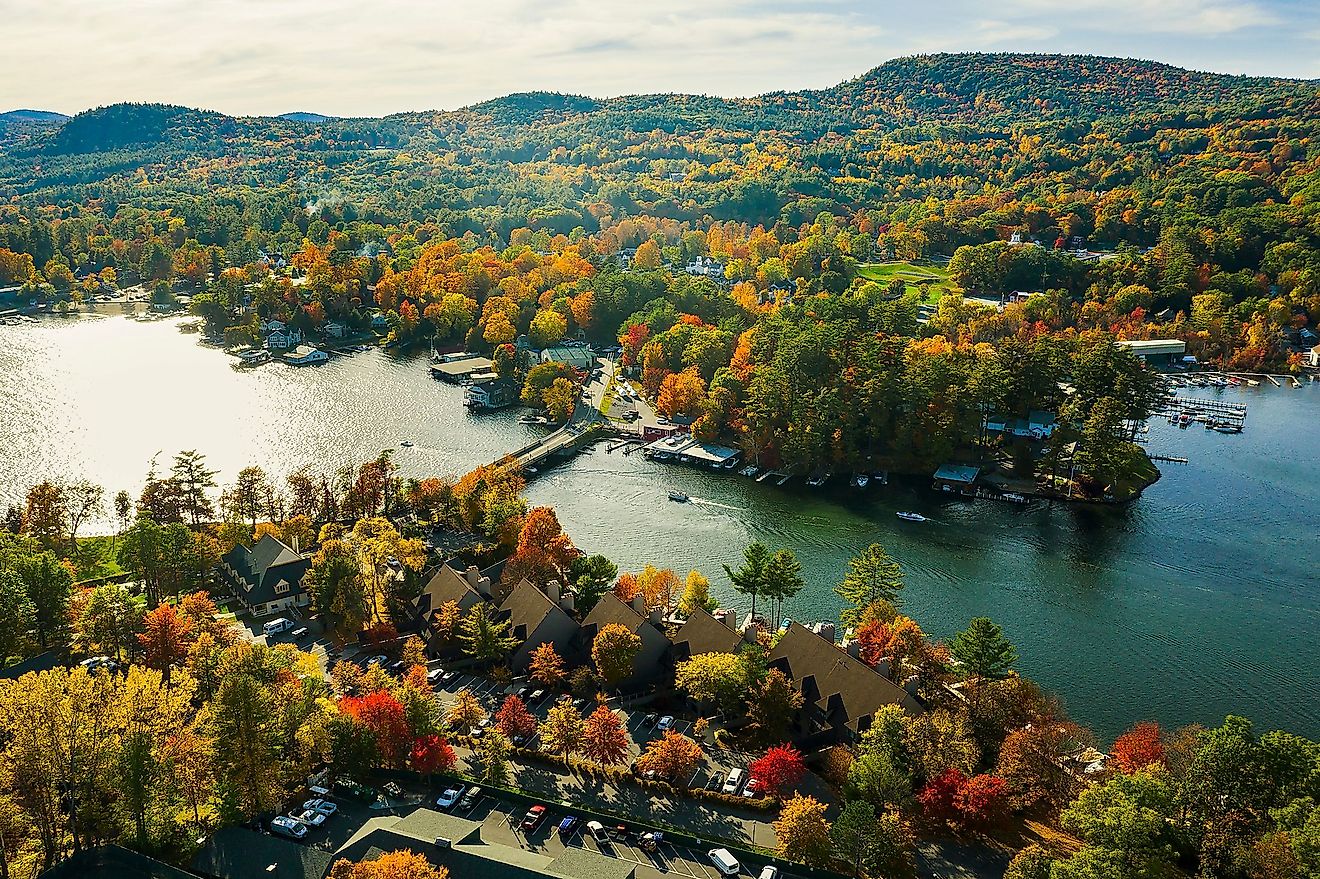
Upstate New York is a vast and picturesque region that lies north of New York City, encompassing rolling hills, towering mountains, and vibrant small towns. Often referred to simply as "Upstate," it includes major cities such as Albany, Buffalo, Rochester, and Syracuse, each with its own distinct character and attractions. Located just a few hours' drive from Manhattan—anywhere from around two to five hours, depending on the destination—this region offers a striking contrast to the fast-paced urban life of the city.
The weather in Upstate New York varies widely by season. Winters are often cold and snowy, especially in areas near the Great Lakes and the Adirondacks, making it a prime location for skiing and other winter sports. Summers are warm and pleasant, perfect for exploring the region's countless hiking trails, waterfalls, and scenic lakes. The autumn season brings a breathtaking display of fall foliage, drawing visitors from around the country.
Whether you're looking for a peaceful nature retreat, an outdoor adventure, or a cultural escape, Upstate New York delivers. Its diverse landscapes, historic landmarks, and welcoming communities make it a must-visit destination for travelers seeking an authentic experience beyond the bright lights of the city.
Geography
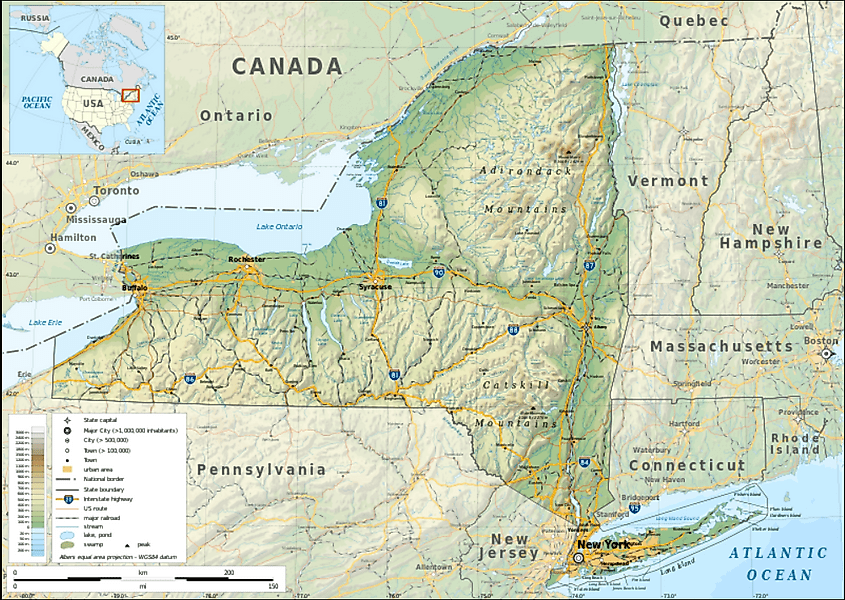
Upstate New York encompasses a large portion of the state, generally considered anything north of the New York City metropolitan area. The region stretches from the Hudson Valley and the Catskills in the south to the Canadian border in the north. It is bordered by Pennsylvania to the south, Vermont, Massachusetts, and Connecticut to the east, and Ontario and Quebec to the northwest. This vast expanse of land is home to a diverse array of landscapes, including mountains, rolling hills, lakes, and river valleys.
Climate

Light snow falling on Lake Placid, lawn chairs and gazebo, State of New York.
Upstate New York experiences a humid continental climate, characterized by cold, snowy winters and warm, humid summers. The region’s weather varies based on elevation and proximity to large bodies of water, such as the Great Lakes. Areas like the Adirondacks can see harsh winters with heavy snowfall, making them a paradise for winter sports enthusiasts. Meanwhile, the Finger Lakes region enjoys a milder climate, making it an excellent destination for wine production and summer getaways.
Major Areas
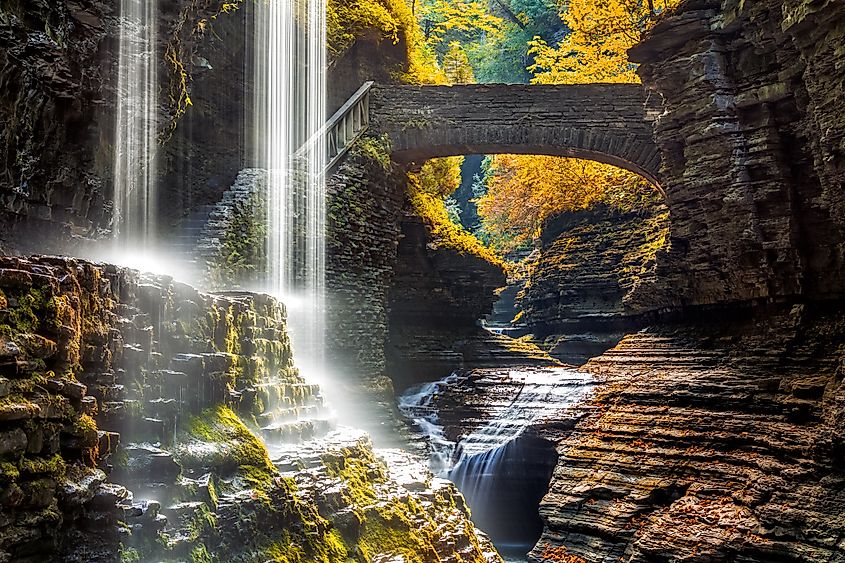

Watkins Glen State Park waterfall canyon in Upstate New York.
Upstate New York is divided into several distinct regions, each with its own unique character and attractions:
-
The Adirondacks: A sprawling mountain range known for its pristine lakes, dense forests, and outdoor recreation. The region is home to Lake Placid, a two-time Winter Olympics host.
-
The Finger Lakes: A collection of 11 long, narrow lakes famous for their wineries, waterfalls, and picturesque landscapes.
-
The Catskills: A mountainous area popular for hiking, camping, and its rich artistic heritage.
-
The Hudson Valley: Known for its charming small towns, apple orchards, and historical sites.
-
The Thousand Islands: A scenic archipelago along the St. Lawrence River, perfect for boating and fishing.
-
Western New York: Home to Niagara Falls, Buffalo, and the Chautauqua Institution, this area blends natural beauty with vibrant city life.
-
The Capital Region: Centered around Albany, this area is rich in history and serves as the political heart of the state.
Population
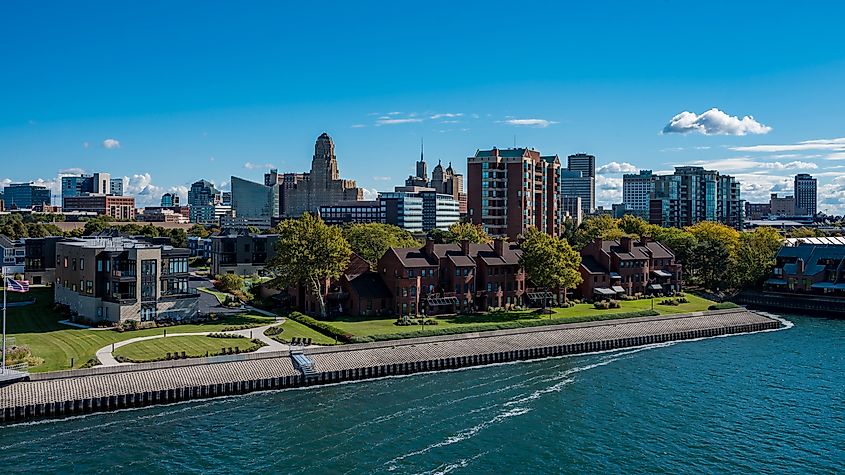

Skyline of Buffalo, New York, in summertime.
While New York City dominates the state's population, Upstate New York is home to about 6 million residents spread across smaller cities, towns, and rural communities. Some of the larger cities include Buffalo, Rochester, Syracuse, and Albany. Despite a lower population density compared to downstate, Upstate New York boasts a high quality of life with strong community ties, affordable housing, and access to outdoor recreation.
Geology

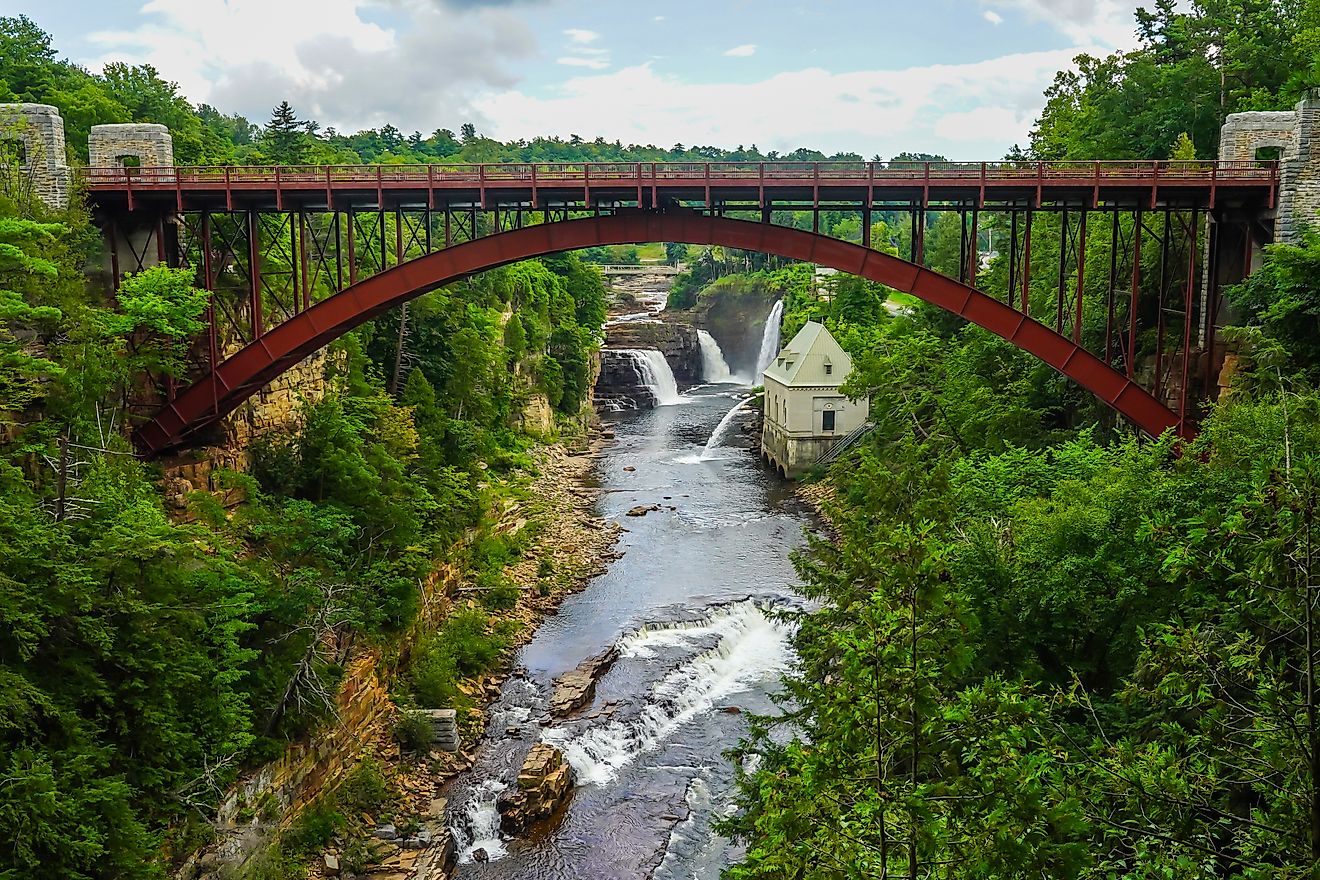
The geological history of Upstate New York is deeply fascinating, shaped by ancient glacial activity, tectonic movements, and erosion. The Adirondack Mountains, one of the oldest mountain ranges in North America, date back over a billion years. The Finger Lakes were carved out by glaciers, creating deep, narrow lakes that now define the region’s landscape.
The Catskill Mountains were formed from sedimentary rock deposits, giving them their distinctive rolling appearance. The presence of numerous waterfalls, caves, and gorges—such as those found in Watkins Glen State Park—further showcase the region’s dynamic geological past.
Flora
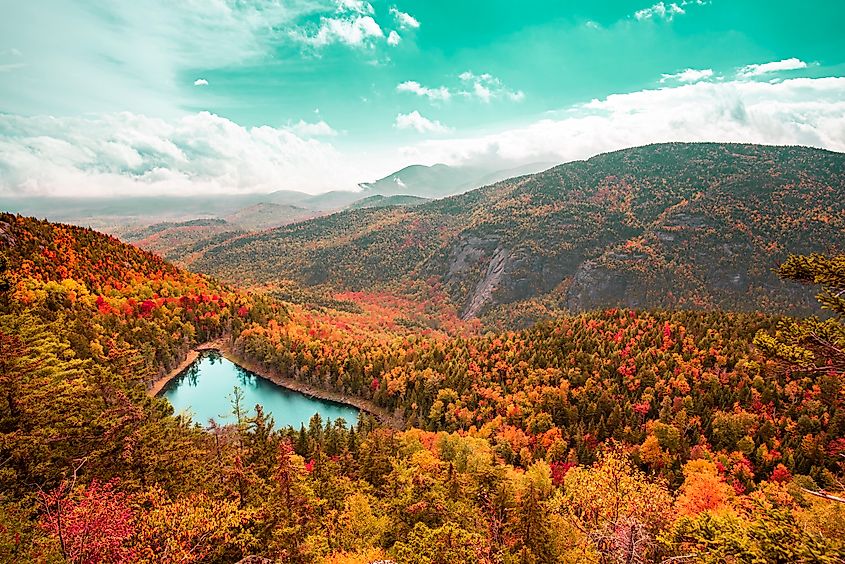

Adirondack Mountains New York in Fall.
The vast and varied landscapes of Upstate New York support a diverse range of plant life. Hardwood forests dominate much of the region, with maple, oak, and birch trees providing stunning fall foliage each year. In the Adirondacks and Catskills, coniferous trees such as spruce, fir, and pine are common.
The Finger Lakes and Hudson Valley regions are home to fertile farmland, with crops like apples, grapes, and corn thriving in the rich soil. Wildflowers, including trilliums and lupines, bloom throughout the state, adding splashes of color to the countryside.
Fauna
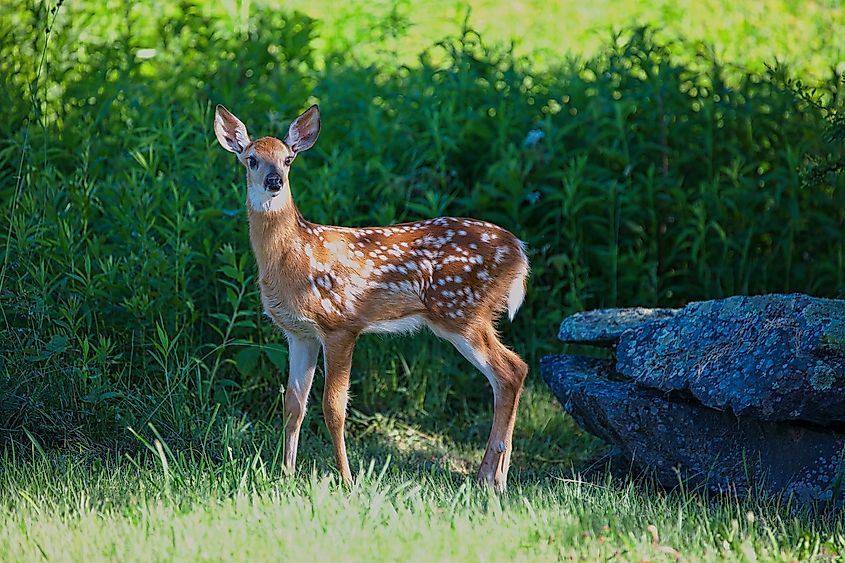

A fawn in Upstate New York.
Upstate New York is a haven for wildlife, offering a home to a variety of animal species. White-tailed deer, black bears, and red foxes roam the forests, while bald eagles and osprey can be spotted soaring over rivers and lakes. The region’s waterways support diverse fish populations, including trout, bass, and salmon, making it a popular destination for anglers. Smaller mammals, such as beavers, otters, and raccoons, are commonly found near rivers and wetlands. Birdwatchers will delight in the wide range of species that call Upstate New York home, from warblers in the summer to snowy owls in the winter.







